A malicious program mainly distributed via mass mailings and designed to inject arbitrary content into webpages loaded in browser windows. The Trojan can take screenshots, download other malicious programs to the infected computer and run them.
Once launched, the Trojan checks whether its copy with another PID is already present in the system and, if so, stops functioning. Then it tries to detect the following running processes of popular anti-virus software and virtual machines: cpf.exe, MsMpEng.exe, msseces.exe, avp.exe, dwengine.exe, ekrn.exe, AvastSvc.exe, avgnt.exe, avgrsx.exe, ccsvchst.exe, Mcshield.exe, bdagent.exe, uiSeAgnt.exe, vmtoolsd.exe, vmacthlp.exe, vpcmap.exe, vmsrvc.exe, vmusrvc.exe, VBoxService.exe.
The Trojan refers to the HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders registry branch to get access to the current user's folder and tries to read its configuration file from this folder. If the attempt fails, the Trojan uses the settings stored in its body. A configuration file can look as follows:
[dfr]
0="vertig***.com"
1="gigacirc***.com"
2="drivee***.com"
3="goog1a***.com"
[scripts]
amg="/amig***.php?i=33"
sfr="/hist***.php"
sfi="ZG9jdW…”Then the Trojan generates a second configuration file containing information on the infected computer. The data is encrypted with a TEA-like algorithm, encoded in Base64, and then sent to the server via a POST request. The server connection is established using either the socket() and connect() functions or the wininet.dll library functions. The ID of the infected computer is generated from a string identifier of the first disk and the MAC address of the network card. From this string, the Trojan calculates the MD5 value using the functions of Windows CryptoAPI. The obtained value in the form of a HEX string is used by the Trojan as a unique identifier.
Data sent by the Trojan to the server can look as follows:
POST /dkcgb/bfbli/ikifm HTTP/1.1
Host: metrika.yandex.ru
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:31.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/31.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: ru-RU,ru;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3
Cache-Control: no-cache
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Connection: Close
Content-Length: 258
efmcg=Nk0QWfL…On 32-bit operating systems, the Trojan launches the explorer.exe process and injects the malicious code into it using NtQueueApcThread. Executed in explorer.exe, the code removes the Trojan's file and then searches for the following processes: amigo.exe, explorer.exe, iexplore.exe, chrome.exe, firefox.exe, opera.exe, browser.exe, minerd.exe. For each process, the Trojan runs the injection code with which it checks the process name. If the Trojan succeeds to inject its code into explorer.exe, three threads carrying payload are launched; if the code is injected into other processes, a routine to intercept API is started.
On 64-bit operating systems, if the Trojan is launched from %MYDOCUMENTS%\CommonData\winhlp31.exe, three threads carrying payload are launched. The first thread installs the Trojan on the system registering it in the autorun list. The second thread waits for the self-removal flag to be set and, if such a flag is set, removes the Trojan. Using the sqlite3.dll library, the third thread deletes cookies of different browsers and requests configuration data from the remote server. The malicious program intercepts not only WinAPI functions but also specific browser functions to inject arbitrary content into webpages.
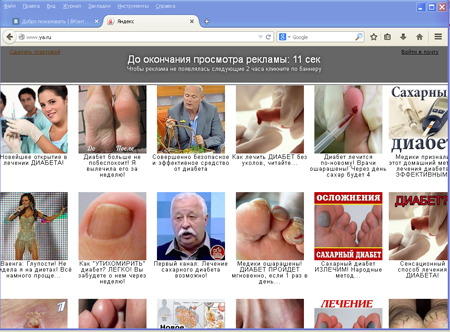
The main purpose of Trojan.Mayachok.18831 is to display advertisements on top of webpages browsed by the user.
The Trojan can also modify the content of the user's profile on social networking websites by posting obscene images and pictures.
If the victim tries to edit the profile, the Trojan urges them to sign up for a paid subscription. In addition to that, the malware can modify the paid subscription form generated by the mobile network operator's website in order to hide important information from the user.