sha1:
- fe612df1ae5fba63ca4eaeb880e9f14b1061636b (version.dll)
Description
A malicious program written in C++ and a component of the Trojan.Scavenger family. It represents a dynamic library that is downloaded by Trojan.Scavenger.2 malware and placed in a target browser’s directory. Its main task is to disable the browser’s protective mechanisms and modify a number of the extensions installed in it.
Operating routine
Trojan launching
The trojan library version.dll exploits the DLL Search Order Hijacking vulnerability and automatically runs when the browser starts up and functions as one of its components.
Checking the running environment
When launched, Trojan.Scavenger.3 finds the main browser process by verifying that the current process has the argument --type. This is to distinguish the main—more privileged—process from the child ones. If the trojan detects the argument --type in the process, it stops working.
Next, Trojan.Scavenger.3 performs an environment check, which is standard for the family. If it detects signs that it is being launched in a virtual environment or debug mode, it stops working.
Hooking the system functions
At the beginning and end of the operation, Trojan.Scavenger.3 installs hooks on the following system functions:
- GetCommandLineW
- CreateFileW
- GetFileAttributesExW
The hook installation technique is splicing.
Hooking the function GetCommandLineW
This hook is for modifying arguments sent to the main browser process when it is launched. The following arguments are added to the command line:
- --no-sandbox — disables the browser’s sandbox initialization, resulting in no isolation of the executed JavaScript code;
- --test-type — launches the browser in a special mode, in which various auto-starts from extensions are disabled.
Patching the Chromium extensions check
To apply this patch, Trojan.Scavenger.3 searches the target library of the Chromium browser engine. To do so, it obtains the list of all of the current process’s loaded modules and tries to find the one with the function CrashForExceptionInNonABICompliantCodeRange (this is the export function from Chromium). If Trojan.Scavenger.3 successfully obtains the module address, it remembers it.
Having found the required address, the trojan reads the code section of the loaded module byte-by-byte, trying to find a match for the required opcode signature:
48 ?? ?? ?? ?? 80 ?? ?? ?? 75 ?? 48 89 CF 80 ?? ?? 01 74 ?? 48 ?? ?? 74 ??This signature is hardcoded in the trojan’s body and consists of 36 bytes; however, the check is only performed on the first 25 bytes.
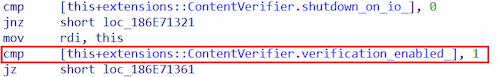
After the code is found, Trojan.Scavenger.3 patches the extensions verification by replacing the value 1 with the value 2:
As a result, the extensions check in the browser is rendered disabled.
Connecting to the C2 server and working with the browser extensions
The first messages between the trojan and the C2 server are packets for creating and checking the encryption key in accordance with the algorithm discussed in the corresponding description for the Trojan.Scavenger family.
Next, the trojan receives from the server the list of browser extensions that are to be modified as well as the modifications themselves. For this, it sends requests to the server via the route /c/c.
Requests with the route /c/c
These requests have parameters that are standard for the family.
The C2 server response depends on which string is sent in the request body; this string is encrypted with an XXTEA algorithm. The following strings can be sent in the request:
- MANU
- BAND|<extension_id>
First, the trojan sends the string MANU. The C2 server responds with the list of IDs for the extensions that the trojan needs to modify:
["bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa", "nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn", "nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb", "hdokiejnpimakedhajhdlcegeplioahd", "opcgpfmipidbgpenhmajoajpbobppdil"]After receiving the list of target extensions, Trojan.Scavenger.3 crawls the directory storing the extensions installed in the browser. Next, it copies the required ones to the directory %TEMP%/ServiceWorkerCache.
After that, the trojan sends the message BAND|<extension_id>. The C2 server responds to it with the JSON that looks like this:
[
{
"file_name": "<the file name or the regular expression>",
"match_helper": "<the string to start searching from>",
"match": "<the string or the regular expression to be changed>",
"replacement": "<the string to be replaced with>"
},...
]Next, Trojan.Scavenger.3 modifies the target extensions. However, it does not modify the original extensions from the directory where they are stored—only the copies of them from its own directory %TEMP%/ServiceWorkerCache. This way, the originals are preserved.
Hooking the functions CreateFileW and GetFileAttributesExW
After modifying the extensions, the trojan hooks the functions CreateFileW and GetFileAttributesExW. These hooks are needed to redirect the work done with the extension files. At this stage, the local paths to the original extension files are substituted with the paths to the modified ones in the directory %TEMP%/ServiceWorkerCache.
More about Trojan.Scavenger.2
News about the trojan
Indicators of compromise