Packer: absent
Compilation date: 2020-14-10
- SHA1 hash: ff82dcadb969307f93d73bbed1b1f46233da762f
Description
The backdoors downloader PlugX, is written in C.
Operating routine
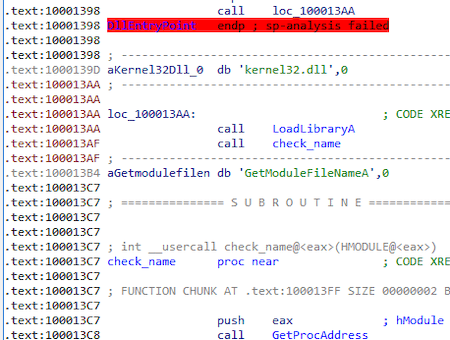
After loading from the main module (msrers.exe) using the LoadLibraryW function, the Trojan loads the kernel32.dll library using the LoadLibraryA[/ string] and gets the address of the exported function GetModuleFileNameA:
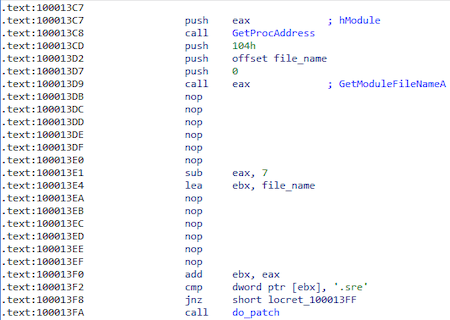
It then obtains the name of the main moduleusing the previously obtained function GetModuleFileNameA and checks if the name contains the substring "ers." (msrers.exe):
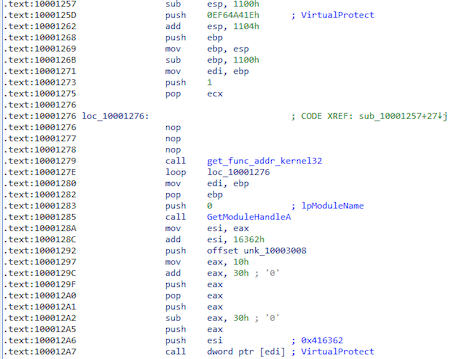
From the hash 0xEF64A41E gets the function VirtualProtect to change the memory access rights to PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE at 0x416362 (msrers. exe):
The following fragment will modify the code at 0x416362 (msrers.exe):
push 0xFFFFFFFF
push 0x100010B0 ; func_addr
ret
Place in the main module to be modified:
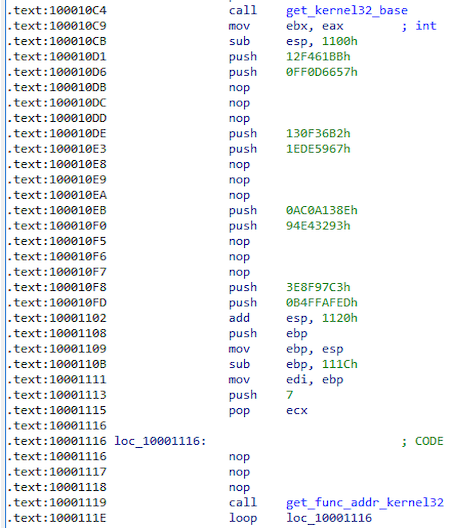
Next, a function is called that receives the base kernel32.dll, as well as the addresses of the functions by hashes.
Script to get a function by hash:
import pefile
ror = lambda val, r_bits, max_bits: \
((val & (2**max_bits-1)) >> r_bits%max_bits) | \
(val << (max_bits-(r_bits%max_bits)) & (2**max_bits-1))
max_bits = 32
library_path_list = [...] # absolute path dlls
def get_func_addr(hash):
for i in xrange(len(library_path_list)):
library = library_path_list[i].split('\\')
name_dll = library[len(library) - 1]
pe = pefile.PE(library_path_list[i])
for exp in pe.DIRECTORY_ENTRY_EXPORT.symbols:
func_name = exp.name
hash_name_func = 0
for j in func_name:
hash_name_func = ord(j) + ror(hash_name_func, 0x07, max_bits)
if (hash_name_func == hash):
print '0x{:08x} -> {} -> {}'.format(hash, name_dll, exp.name)
return
Received features:
| Function name | Hash |
|---|---|
| VirtualProtect | 0xEF64A41E |
| GetLastError | 0x12F461BB |
| CloseHandle | 0xFF0D6657 |
| ReadFile | 0x130F36B2 |
| VirtualAlloc | 0x1EDE5967 |
| GetFileSize | 0xAC0A138E |
| CreateFileA | 0x94E43293 |
| lstrcat | 0x3E8F97C3 |
| GetModuleFileNameA | 0xB4FFAFED |
In the following, the following structure is used to call these functions:
struct api_addr {
DWORD (__stdcall *GetModuleFileNameA)(HMODULE, LPSTR, DWORD);
LPSTR (__stdcall *lstrcat)(LPSTR, LPCSTR);
HANDLE (__stdcall *CreateFileA)(LPCSTR, DWORD, DWORD, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES, DWORD, DWORD, HANDLE);
DWORD (__stdcall *GetFileSize)(HANDLE, LPDWORD);
LPVOID (__stdcall *VirtualAlloc)(LPVOID, SIZE_T, DWORD, DWORD);
BOOL (__stdcall *ReadFile)(HANDLE, LPVOID, DWORD, LPDWORD, LPOVERLAPPED);
BOOL (__stdcall *CloseHandle)(HANDLE);
DWORD (__stdcall *GetLastError)();
};
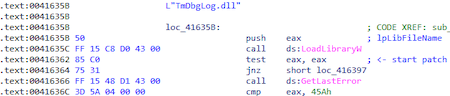
Trojan takes the name dll (TmDbgLog.dll) and adds the ".TSC" extension to it. Next, it opens the file TmDbgLog.dll.TSC for reading and decrypts its contents, which turns out to be a shellcode.
After decrypting the shellcode (TmDbgLog.dll), the Trojan starts executing it:
This is how the script for decrypting the shellcode looks like:
enc = bytearray(open('TmDbgLog.dll.TSC', 'rb').read())
dec = bytearray()
for i in xrange(len(enc)):
dec.append(((enc[i] ^ 0xbb) - 1) & 0xff)
open('TmDbgLog.dll.TSC.dec', 'wb').write(dec)
Before decrypting and running the payload, the shellcode assembles the following structure:
struct st_mw {
DWORD magic;
DWORD *shell_base;
DWORD shell_size;
DWORD *enc_payload;
DWORD enc_payload_size;
DWORD *enc_config;
DWORD enc_config_size;
DWORD *payload_entry;
};
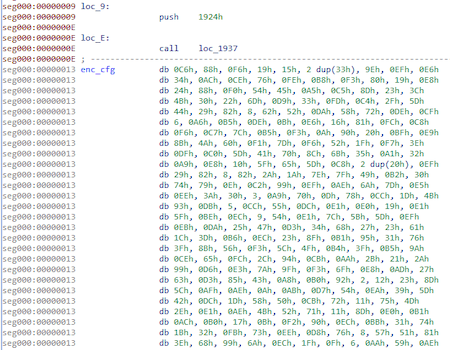
This is what the encrypted config looks like:
The decryption of the config will be done directly in the payload:
import struct
enc = open('enc_cfg', 'rb').read()
key, = struct.unpack('I', enc[0:4])
key1 = key
key2 = key
key3 = key
dec = bytearray()
for i in xrange(len(enc)):
key = (key + (key >> 3) - 0x11111111) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key1 = (key1 + (key1 >> 5) - 0x22222222) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key2 = (key2 + 0x33333333 - (key2 << 7)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key3 = (key3 + 0x44444444 - (key3 << 9)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
dec.append(ord(enc[i]) ^ (key + key1 + key2 + key3) & 0xFF)
open('dec_cfg', 'wb').write(dec)
And it will look like this:
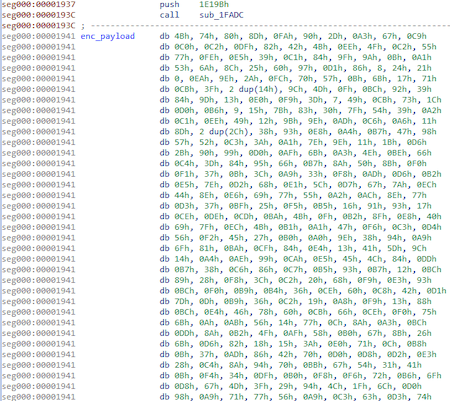
Encrypted payload:
Script to decrypt the payload:
import struct
import struct
enc = open('enc_payload', 'rb').read()
key, = struct.unpack('I', enc[0:4])
key1 = key
key2 = key
key3 = key
dec = bytearray()
for i in xrange(len(enc)):
key = (key + (key >> 3) + 0x55555556) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key1 = (key1 + (key1 >> 5) + 0x44444445) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key2 = (key2 + 0xCCCCCCCC - (key2 << 7)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
key3 = (key3 + 0xDDDDDDDD - (key3 << 9)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
dec.append(ord(enc[i]) ^ (key + key1 + key2 + key3) & 0xFF)
d = bytes(dec)
uncompress_size, = struct.unpack('I', d[8:12])
buf_decompressed = ctypes.create_string_buffer(uncompress_size)
final_size = ctypes.c_ulong(0)
ctypes.windll.ntdll.RtlDecompressBuffer(2, buf_decompressed, ctypes.sizeof(buf_decompressed), ctypes.c_char_p(d[0x10:]), len(d), ctypes.byref(final_size))
open('dec_payload', 'wb').write(buf_decompressed)
After decrypting the payload, the shellcode transfers control to the trojan, with the previously assembled structure st_mw acting as one of the parameters:
Further, trojan works in the same way as the backdoor BackDoor.PlugX.28.