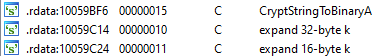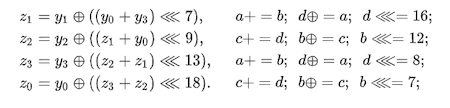Packer: absent
Keys: absent
SHA1 hash:
- aee131ba1bfc4b6fa1961a7336e43d667086ebd2c7ff81029e14b2bf47d9f3a7
Description
A trojan-encoder that operates in the 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It is an executable library written in C++. It uses ChaCha20 and RSA algorithms to encrypt user files. It was first spotted in July 2020. Trojan.Encoder.33222 is a further development of the Maze and Sekhmet encoders, with which it has a lot in common. It is used for targeted attacks on the corporate sector. The encoder’s original name is Egregor Ransomware.
Operating routine
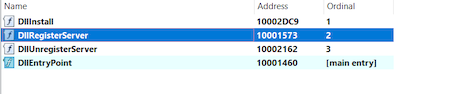
The studied sample is an executable DLL file with the original entry point and three exported functions:
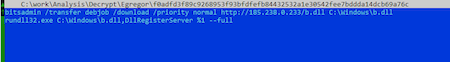
The static analysis shows that malicious activity is contained in the DllRegisterServer function. When running the sample on virtual machines, the trojan program is not executed. Since the encoder is designed for targeted attacks, we assume that it is run on command via the command line. For the initial launch, the rundll32.exe C:\Windows\%SAMPLE%, DllRegisterServer -passegregor10 command is used.
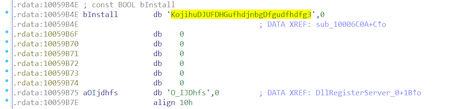
After that, the trojan launches the payload, having previously decrypted it with the same algorithm that is used to encrypt user files (ChaCha20). However, in this case, the key and the nonce are accessible. Decryption requires the KojihuDJUFDHGufhdjnbgDfgudfhdfg3 32-byte string as the key and the O_IJDhfs 8-byte string as the nonce:
The payload content is hardcoded in the trojan body and encrypted:
The payload is a loader in the form of a powershell script that connects to amajai-technologies.industries. At the time of analysis, this server was no longer responding, and the file being uploaded remains unknown. With that, it is worth noting that ransomware operators could steal information through this server. The functionality to operate printers for printing ransom notes in the examined sample was not found and may be contained in the downloaded file.
To start further encryption, a batch file is used, which runs the encoder with the DllRegisterServer function, but with different command-line parameters:
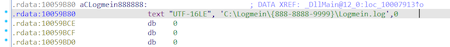
The payload in the system is disguised as LogMeIn products:
It should be noted that the encoder uses the ChaCha20 algorithm (a type of Salsa20 cipher), and not AES, as it is written in some sources. This is confirmed by the expand 16-byte k and expand 32-byte k strings:
The use of ChaCha20 is also indicated by the encryption algorithm in the quarter-round function:
Below is a comparison between quarter-round of Salsa20 (left) and ChaCha20 (right):
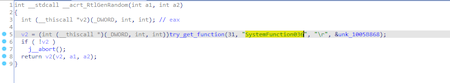
To generate the key RtlGenRandom function via the SystemFunction036 call is used. The generator based on RtlGenRandom is considered as cryptographically secure. In this case the decryption is not possible:
Most of the code is written manually and obfuscated, which complicates the analysis. The information about the project’s original location is stored in the debugging data: M:\sc\p\testbuild.pdb.
One of the features of this encoder is that the extensions of each file differ even within the same computer. Similar to Sekhmet, a new random extension is used for each file. To identify encrypted files, a four DWORD file marker is used at the end of the file (EOF): 00 00 00 00, 00 00 XX XX, 00 00 XX XX, XX XX 6B B1 (bytes instead of XX are different for each file). Using these values, one can determine that the file was infected by this particular encoder.
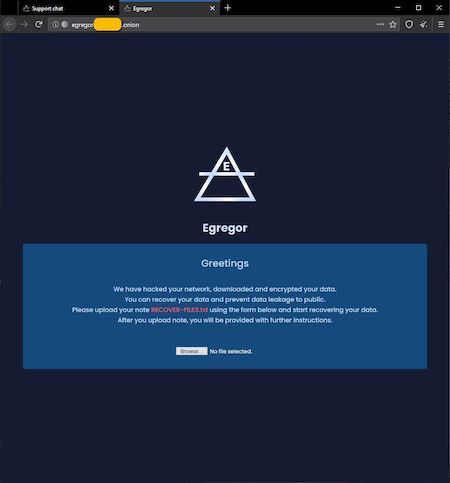
Clicking on the link provided by the ransomware after infection leads to the operator’s page, accessible through the Tor network.